Connect to GitHub Using SSH
What is SSH?
You can connect and authenticate to remote serves such as GitHub without supplying your username and password during each visit. It is recommended that you review your SSH key regularly and revoke any that may be invalid or compromised, just as you would your email account.
Check for existing SSH Keys
$ ls -al ~/.ssh
This lists all your available SSH keys. Check to see if you have a public SSH key. The file naming, by default, could be as follows:
id_rsa.pub
Generate a new SSH key
If you have none listed from the step above, you may want to generate a public and a private key pair:
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "<your GitHub email address goes here>"
This will create a new ssh key using the email you have provided. When prompted to enter a file to save your ssh key, just press Enter to save it in the default file location.
Enter a file in which to save the key (/home/you/.ssh/id_rsa): [Press enter]
Type a secure passphrase when prompted.
Adding your SSH key to the ssh-agent
In the background, you can start your ssh-agent as below:
$ eval "$(ssh-agent -s)" $ ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa
id_rsa is the file that holds your key. Check how to list your files above. This file is hidden hence the use of ~/.
Adding your SSH key to your GitHub account
Copy your ssh key to your clipboard (ctrl + shift + C from your terminal). Make sure not to add newlines or whitespaces while you copy to the clipboard by running the commands shown below:
$ sudo apt install xclip
This downloads and install xclip.
$ xclip -sel clip < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
This copies the content of the _idrsa.pub file to your clipboard. You can substitute the file name to match the exact name in your system.
Short and Easy Method
If the method above does not work very well for you, consider doing the following:
Generate SSH key using:
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your email".Copy the output of the command below to your clipboard:
$ cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub # This will display the key in your terminal # Make sure not to add newlines or whitespaces- Paste the above-copied output to the form at https://github.com/settings/ssh/new.
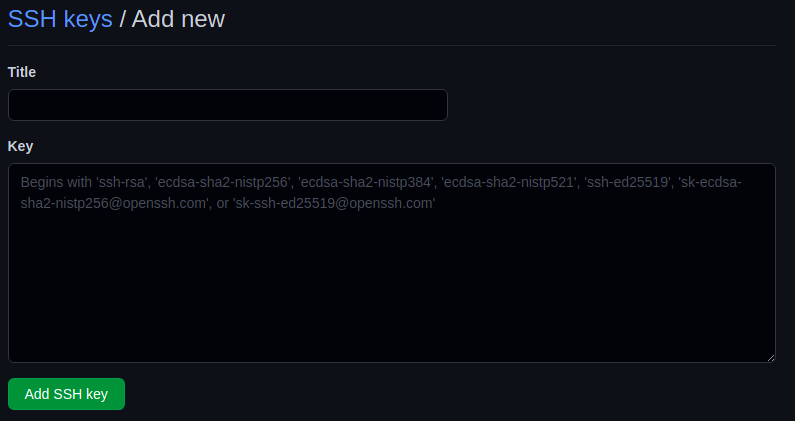
Update Your GitHub SSH Key
- Log into your GitHub account. Click on settings as shown in the image below:
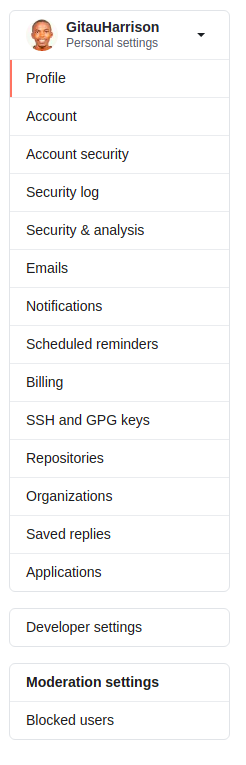
- Click on SSH and GPG keys from the left menu with Settings
- Click the green New SSH key or Add SSH key button

- Paste your valid
sshkey into the Key field
HTTPS and SSH remote's URL
If you look at one of your GitHub repository, you will see a green Code button . Click on the drop down menu to locate HTTPS, SSH and GitHub CLI
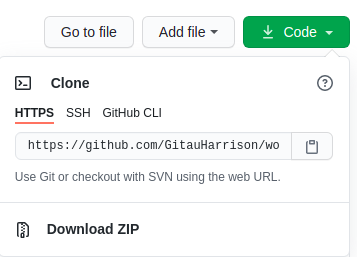
-
If you are updating to
https, your URL will look as below:https://github.com/GitauHarrison/work_gossip_chat_app.git -
If you are updating to
ssh, your URL will look as below:git@github.com:GitauHarrison/work_gossip_chat_app.git -
If you are updating to
GitHub CLI, your URL will look as below:gh repo clone GitauHarrison/work_gossip_chat_app
Testing your SSH connection
$ ssh -T git@github.com
This command will attempt to ssh to GitHub. You may see a warning.
- Verify the fingerprint and then type yes
- Verify that the resulting message contains your username
Working with ssh passphrases
To add extra layer of security, you will need a passphrase to your ssh. The reason behind this is because whenever someone gains access to your computer, they also gain access to every system that uses that key. ssh-agents are used to securely save your passphrases so you don't have to enter it all over again.
To add or change your passphrases for your existing private key without generating a new keypair, run the command below:
$ ssh-keygen -p
Press Enter to save your file in the default location, type in your new passphrase and press Enter again.
Additional Notes
Switching remote URL from SSH to HTTPS
As ealier noted, whenever you use https, you will be prompted to provide your GitHub username and password
List all your remotes to know what remote name you want to change:
$ git remote -VChange to
HTTPS:$ git remote set-url origin https://github.com/GitauHarrison/work_gossip_chat_app.gitReplace
https://github.com/GitauHarrison/work_gossip_chat_app.gitwith your own repo link.Verify remote URL has changed:
$ git remote -V
Switching remote URL from HTTPS to SSH
The commands needed for this are similar as those above. Run each at a time:
$ git remote -v $ git remote set-url origin git@github.com:GitauHarrison/work_gossip_chat_app.git $ git remote -v
You can refer to GitHub's documentation to learn more.
Share
If you enjoyed this article, you can share it with another person.
TweetNewsletter Subcription
Level up your skills.
We take your privacy seriously. Read our privacy policy. Unsubscribe | Resubscribe.




